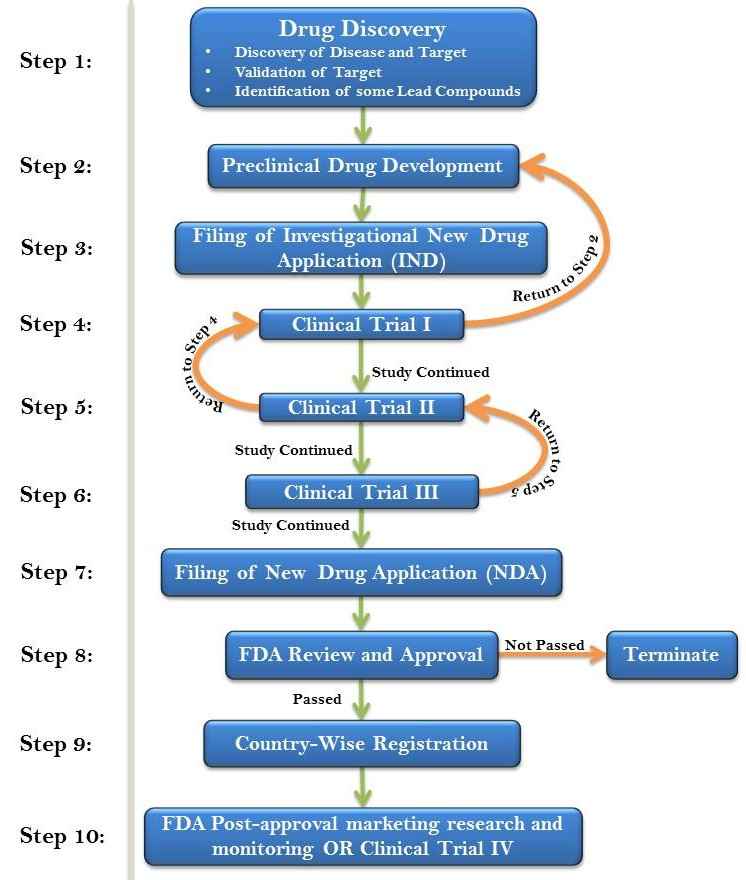
The USFDA drug discovery and drug development process is a long and a complex one. There are certain steps that are followed to complete the process. The whole process can take years to get approval for drug, but efforts and time is worth the result.
On an average, the whole process can cost a pharmaceutical company $2.6 billion and it can take around 10 to 12 years for the whole process to be successfully done. The drug discovery and development process is divided into five different stages. These stages are as follows
Drug Discovery
Preclinical Drug Development
IND Application (Investigational New Drug)
Clinical Development
NDA (New Drug Application)
FDA Review and Approval
Country-wise Registration
FDA Post-approval marketing research and monitoring
Flow Chart depicting the process in brief
#1. Drug Discovery
The drug discovery process involves four different levels, including
Discovery of Target
Initial phase of drug discovery is termed as Target Discovery. In this stage, in-vitro research is done for identifying the target that is involved in certain diseases. Target is the molecule which is integral to intracellular signaling or gene regulation. To choose a target molecule of your research, you need to make sure that molecule can be used as a drug.
Validation of Target
When you have selected a possible target, you have to demonstrate that the target is involved in the process of progression of a particular disease and that the activity of the target molecule can be easily regulated. This is essential to make drug development process successful in the coming stages.
Identification of Lead Compound
This process involves identification of a compound which can interact with the selected target. Different screening experiments can be done to select the natural compound which can be re-purposed like drugs. Synthetic compounds can also be designed that can target the potential target and not interfere in other processes that takes place in the cells. Mechanism of action of the target has to be tested along with some safety tests, which are regulated in a cell culture.
Lead Optimization
When one or more lead compounds are identified, optimization has to be done for safety and efficacy purpose. To prevent binding of synthetic molecules to off-target molecules, the design of these molecules can be altered. Testing of optimal dosage and route of administration is performed on both two and three dimensional cell cultures. A safety test is also done in this stage before introducing it in in-vivo animal models.
#2. Preclinical Drug Development
This stage includes an extensive testing of lead compound or drug on animal models. This is done to ensure that drug is safe to use on these animals and later it will be safe to use in human trials as well. In this step, side effects are also noted and addressed. To make the drug development process move forward, the FDA needs extensive data and testing. The animal models that are used in this stage include genetically modified mice or knockout mice.
#3. IND Application (Investigational New Drug)
Before entering into clinical trials, an IND (Investigational New Drug) application has to be submitted to FDA. When this application is filed, you can proceed with clinical trials if FDA has not reported negatively about new drug.
#4. Clinical Development
When preclinical research is done, drug can move on to the clinical drug development. There are mainly three phases of clinical trials.
Phase I Clinical Trial
This is the first phase of clinical trial in which drug is tested on less than hundred healthy patients in order to determine the safety. It also involves carcinogenicity testing, which is performed in a mouse model. The commonly used model for this testing is Tg rasH2 mouse. Once, drug passes the safety and carcinogenicity test, it enters into next phase of clinical trial.
Phase II Clinical Trial
In this phase the number of patients increases and is 100 to 500. This phase is responsible for studying the effectiveness the drug. Patients that are present in this phase are the ones who have disease which the drug is trying to treat. In this phase, the side effects, efficacy and adverse events of new drug are tested. The analysis of optimal dosage of drug also takes place in this step.
Phase III Clinical Trial
This is considered to be the most important phase that every new drug has to pass. According to the studies, it is shown that only 12% of new drugs pass this stage. In this phase, numbers of patients are between 1000 and 5000. The data obtained from this phase are further used to label future prescription of new drug.
#5. NDA (New Drug Application)
Once clinical trials are done, NDA (New Drug Application) has to be filed and submitted to FDA. When NDA is filed, FDA will review the details and will decide whether the drug will be approved or not. This is used to demonstrate that clinical trials have proved the efficacy and safety, and is qualified for marketing.
All the information related to the drug, including all studies, data of preclinical and clinical studies, interactions with other drugs, precautions, and side effects. This review process can easily take six to ten months. When the drug is approved by FDA, the labeling process of it starts.
#6 FDA Review
When results from the three phases of clinical trials are obtained and the drug has been appropriately formulated for a good safety and efficacy, it is forwarded for being reviewed by FDA (Food and Drug Administration). This is the time when FDA will review the drug and will come to a decision.
#7. Country-wise Registration
When a drug is approved from USFDA, you have to register it in those countries where you want to sell it. All countries have different guidelines for registering drugs.
#8. Post-Approval Marketing Research and Monitoring
When the drug is approved and is ready to be manufactured at a big scale, the drug companies have to monitor safety of drug with the help of FAERS (FDA Adverse Event Reporting System) database. FAERS makes it easy for FDA to determine the post-marketing safety of the drug.